
FICO scores are an indicator of a person's credit history. They are used by creditors to look at existing debt and income. A good credit rating gives you more options and allows you to get lower interest rates. Your credit score may also be used by landlords and utility companies. If you don't have a good score, you may need to improve your credit score if you want to apply for a loan or get a new credit card.
History of payments
Credit scores are influenced by your payment record. It keeps track of when and how much debts have been paid. You will see fewer negative entries over time. The latest FICO model also incorporates trended data covering the past 24 months. This can help lenders assess if your ability to repay your debt completely.
Your payment history is the history of all your payments. This gives lenders an overview of your repayment history. Your credit score can be seriously damaged if you miss a payment or send one to collections. This is because lenders view you as a high-risk borrower if you don't make payments on time.
Accounts owing
Credit score is affected by how many accounts you have. This category represents 30% of your total score. New credit card accounts directly impact this number. It also includes the types of accounts you have and their balances. Your risk of being overextended is higher if you have more accounts.

You can improve your credit score by paying off your debt. Credit scoring models consider many factors when determining a person’s credit score. Although debt is not necessarily a sign of a high risk, it can make it more difficult for you to pay your monthly obligations.
Credit history length
The length of credit history is one important factor that determines your credit score. Your credit score includes the age of each account as well as its length. A minimum of six months is a good time to have a credit history. If you have just opened a new bank account, however, your credit history will be significantly shorter.
FICO uses the average account age to determine your credit history. This figure can be calculated by adding each account's ages and dividing it by the total number. The average credit account age is 8 years. In determining the length and duration of your credit history, you also need to consider the lengths of particular accounts as well as the time they have been open. FICO does not disclose these factors.
New credit
FICO scores will consider recent activity such as when you applied for credit or opened new accounts. Lenders will also take into account the time since your last application for a new credit card and this may affect your score by a few percentage points. The type of activity that affects your score depends on the type of account you apply for and the amount of credit you are applying for.
Good news is that you can improve your score by paying your bills in time and responsibly using credit. Start by checking your credit report. Luckily, you can get your reports in less than two days. You can also monitor your credit by setting up due date alerts on your credit cards bills. While this can be time-consuming, it is an excellent way to improve credit scores.
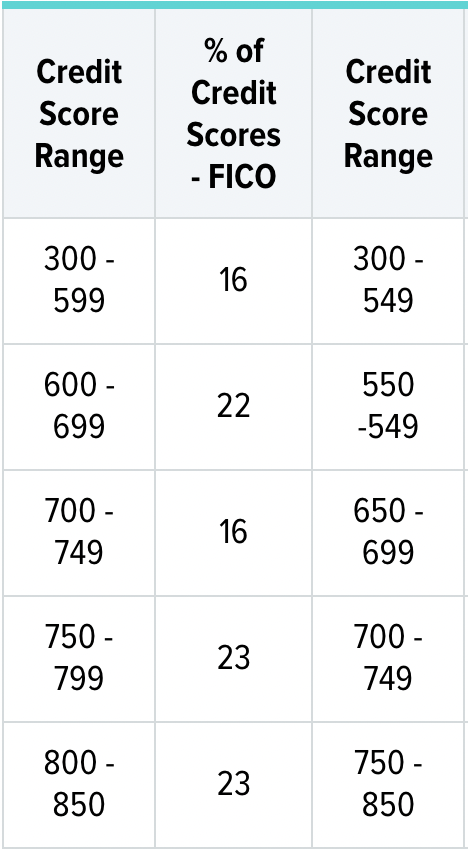
VantageScore
VantageScore is a credit rating that was first introduced in 2006. It is based on credit reports, just like FICO. However, VantageScore is different in how the credit score is calculated. FICO draws its data from credit bureaus. VantageScore is based on data that covers consumer behavior over a 2-year period. Consumers need to be able to distinguish between FICO and VantageScore scores and understand their impact on each other.
VantageScore comes with its own advantages and disadvantages. It is simpler to comprehend and compare. Equifax, Experian and Transunion developed the VantageScore system with the aim of making it consistent and more understandable. It uses letter grades rather than numbers.